What Is Audiology
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds.
Entry Requirements To Study Audiology In South Africa
Matriculation exemption.
Pass in English at level 4.
Pass in Physical Science OR Life Sciences at level 4.
Pass in Mathematics at level 4 OR in Mathematical
Literacy at level 5.
Pass in 3 other subjects (excluding Life Orientation)
at level 4.
Audiology is the profession dealing with the assessment and management of hearing, hearing loss, and ear-related balance disorders. The audiologist is also involved in promoting healthy ear and hearing habits, and preventing or minimizing disability due to hearing loss or balance disorders. Audiology is one of the
fastest-growing health professions, due to rapid technological advancements.
Audiologists:
measure and diagnose hearing ability.
provide rehabilitative services to children and adults with a hearing loss.
fit hearing aids and assistive listening devices.
consult on issues concerning noise-induced hearing loss, and develop hearing conservation programmes.
manage individuals with auditory processing difficulties.
manage people with ear-related balance problems.
serve as expert witnesses in litigation related to their areas of expertise.
aim to prevent and/or minimise hearing loss and its effects.
conduct research on hearing and the balance system.
Information about the BSc in Audiology
If you thrive on challenges and want to assist people in improving their quality of life, Audiology is a profession that could fulfil those needs. You can choose to work across the age spectrum, or work only with adults or children (an audiologist can even do a hearing test on a one-hour old baby). The ability to speak African languages, in addition to English, is a valuable resource in providing audiology services.
The BSc in Audiology is a four-year course of full time study. Your training involves the medical, scientific, social and psychological aspects of hearing, speech and language.
You will learn about the anatomy and physiology of hearing; normal communication development; early intervention; assessment and management for child and adult clients with different hearing or balance problems.
The Audiology programme is one of two programmes offered by the Division of Communication Sciences and Disorders, the other one being Speech-Language Pathology. Some courses during the four years of study are common.
Speech-Language Pathology and Audiology fall into the broad area of communication sciences and disorders. These are two separate but related professions and are studied as two separate degree programmes. If you obtain the BSc Audiology degree, you will be registered with the Health Professions Council as an audiologist.
Audiology training in South Africa
Audiology training programmes are delivered through five accredited universities in South Africa (RSA) and these are typically associated with programmes in speech-language pathology. The programmes are usually housed within the faculties of health sciences, or located within the education department of the respective institutions.
Audiology as a healthcare profession is governed by the Health Professions Council of South Africa (HPCSA) and, in order to practise as an audiologist, students and graduates must register with the HPCSA and adhere to its requirements for clinical and professional practice.
The HPCSA is the professional board for most healthcare professions in RSA and each profession is represented by its own professional board who is responsible for registration, the quality of education and training, ongoing professional development, ethical guidelines and practice, and compliance with professional standards.
Professionals who work within the stated scope of practice are required by law to register with the HPCSA and failure to do so is considered a criminal act.
Audiology programmes in RSA are delivered in the format of a four-year undergraduate course. Historically, audiology courses were offered alongside speech-language pathology and graduates were dually trained and able to qualify as both audiologists (AUD) and speech-language therapists (SLT). After 1998, many university programmes started to separate the programmes into single-profession tracks, leading to qualification as either an audiologist or speech-language therapist.
“Most courses in RSA continue to have some joint teaching and shared modules between SLT and AUD students, allowing for the development of strong interprofessional links.”
Today, the majority of universities offer these courses separately, with the exception of WITS University and Sefako Makgatho University, who currently still offer a joint programme. WITS University is in the process of splitting their programme and plan to offer separate courses from 2018.
The entry requirements for audiology training in RSA typically involve matriculation endorsement (a final high school pass rate that is the minimum entry level for studying a bachelor’s degree at university) with completed subjects like Maths / Maths literacy, English, and Physical / Life sciences.
Most courses in RSA continue to have some joint teaching and shared modules between SLT and AUD students, allowing for the development of strong interprofessional links that are important for children and adults with hearing, balance and communication difficulties.
At the University of Cape Town, first, second, and third year SLT and AUD students have joint modules in child language, pediatric aural rehabilitation, sign language, isiXhosa / Afrikaans (languages), linguistics, early communication intervention, speech and hearing sciences, human communication development, anatomy, psychology, becoming a health professional, and research methods and statistics.
In addition, students are also required to work together in fourth year on advanced seminars, writing and presenting on topics that are relevant to both professions e.g. managing difficult clinical encounters, provision of culturally sensitive services, attributes of the successful clinician etc.
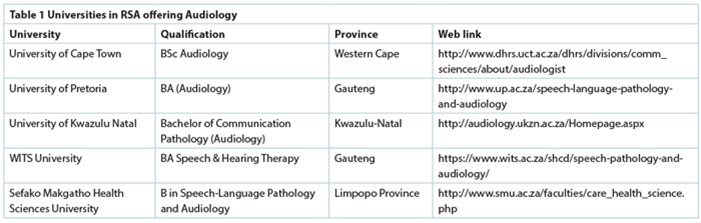
Table 1 provides an overview of the six universities who offer training in audiology and hearing therapy in RSA.
Clinical training of audiologists typically starts early in the degree programme (second year) and increase over the course of the programme. Students are required to obtain 400 hours of clinical work, which is carefully planned and monitored, to ensure that they are able to register with the HPCSA at the end of their final year of study.
Clinical hours are recorded for assessment, intervention, observation and case discussions. Of the 400 clinical hours, 375 must come from clinical contact, and 25 from observations. Students are exposed to a variety of clinical audiology functions throughout their four-year training, including community clinics, hospital clinics, university clinics, simulation clinics, schools for the deaf, and institutions like Deaf SA.
The training, education and clinical practice of audiologists in RSA is challenging given the rich cultural diversity and 11 official languages of the country.”
In RSA, registration with professional organizations is done on a voluntary basis. There are currently two professional organizations that audiologists are able to join: South African Association of Audiologists (SAAA) and South African Speech-Language-Hearing Association (SASLHA).
The role of these organizations is to promote the professions of audiology and speech-language pathology, offer opportunities for further professional development, publish a peer-reviewed academic journal (South African Journal of Communication Disorders), and provide guidelines for professional and ethical practice.
The training, education and clinical practice of audiologists in RSA is challenging given the rich cultural diversity and 11 official languages of the country. Geographic and socio-economic differences also add to the complexity of hearing health service delivery in a developing world context. Students typically graduate with a deep appreciation of cultural diversity, as well as the ability to creatively apply their theoretical knowledge to the local needs and context.
Schools Offering Audiology In South Africa
What requirements are needed to study audiology in South Africa ?
The graduate programme typically requires four years to complete; applicants must hold a bachelor’s degree to qualify, preferably in a medically-related field. Most audiology programmes include an internship or other clinical practice opportunity.
How long does it take to become an audiologist in South Africa?
four-year
Audiology Audiologists assess, advise, and provide rehabilitative services to children and adults with hearing and balance disorders, and related communication difficulties. In the four-year Bachelor of Audiology programme, you will major in Audiology and Psychology.
What is the minimum qualification required to practice as an audiologist?
Audiologists must earn at doctoral degree in the field in order to become licensed and certified. That requires a four-year bachelor’s degree followed by four years in a doctor of audiology program.
How much are audiologist paid in South Africa?
R363,777 (ZAR)/yr.
How many years does it take to be an audiologist in South Africa ?
four years
It generally takes four years to become an audiologist after completing a bachelor’s degree. These professionals are required to have a Doctor of Audiology (AuD) Degree which takes four years to complete.
How many audiologists are there in South Africa?
The HPCSA database had a total number of 3266 registered Audiologists, Speech Therapists and Speech Therapists and Audiologists. Most were registered as Aud-STs (46.8%) followed by STs (33.3%) and Auds (18.9%).
Do audiologists go to medical school in South Africa ?
What kind of training do audiologists have? to schools to hospitals. All new audiologists are required to have a doctor of audiology (AuD) degree. Typically it takes four years to complete this post-graduate degree.
Is it worth it to become an audiologist in South Africa ?
Audiologists play a very valuable role in society. They assist those with hearing challenges as well as their family members. It can be an extremely rewarding career, but it can also be quite stressful.
What are the disadvantages of being an audiologist in South Africa ?
Cons of Audiology
Long length and high cost of education. Becoming an audiologist takes many years of education—and lots of money.
Conditions of the ear can be delicate to diagnose and treat. .
Working with very young children or the very elderly.
Will audiologists be needed in the future in South Africa ?
Employment of audiologists is projected to grow 20 percent from 2016 to 2026, much faster than the average for all occupations. However, because it is a small occupation, the fast growth will result in only about 3,000 new jobs over the 10-year period.
